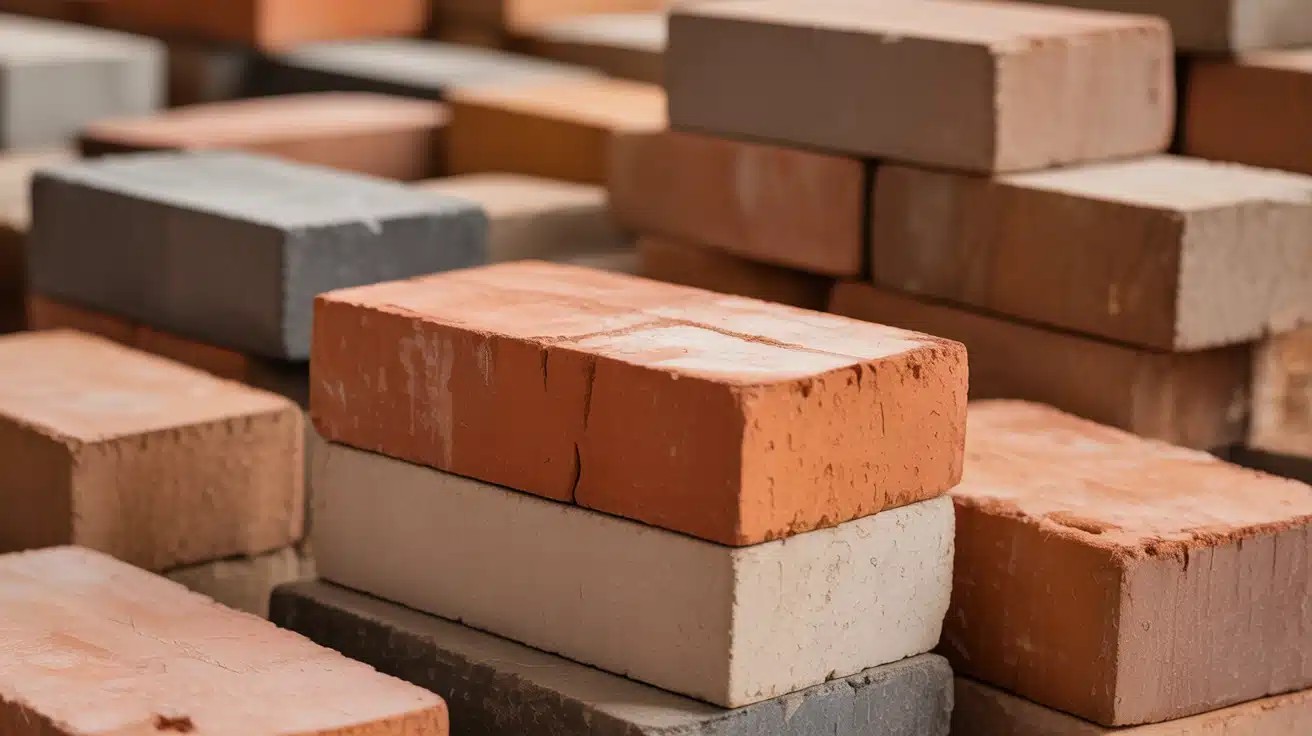
Bricks are everywhere. You see them in homes, walls, and buildings. But what are they actually made of?
Most people never think about it. They just see the finished red blocks.
This guide explains what bricks are made of and how they’re manufactured. You’ll learn about different types, standard sizes, and what affects their quality.
Let’s find out what’s in those walls around you.
Bricks Composition
Bricks are made from clay. That’s the main ingredient.
- Clay is a natural soil material. It gets soft when wet and hard when heated.
- Shale is often mixed with clay. It’s a type of rock with similar properties.
- Water makes the clay workable. You need it to shape the bricks.
- Sand gets added to prevent cracking. It also makes bricks stronger.
- Iron oxide is naturally found in clay. This gives bricks their red color.
The process is simple. Mix these materials together. Press them into molds. Let them dry. Then fire them in a kiln at 900-1200 degrees Celsius. The heat turns soft clay into hard brick.
That’s it. Clay, water, sand, and heat create the bricks we use in construction.
How are they Made?
Making bricks follows a simple process. Let me walk you through each step.
Step 1: Mining the Clay
Workers dig clay from the ground. They use excavators to remove it from quarries. The clay often contains shale, too.
Step 2: Preparing the Material
The clay goes through crushing machines. These break down large chunks into fine particles. Workers remove stones and debris. Then they add water to make it workable.
Step 3: Mixing
Machines mix the clay with water and sand. This creates a uniform paste. The consistency needs to be just right for molding.
Step 4: Shaping
The clay mixture goes into molds. There are two main methods. One uses machines that press clay into shapes. The other pushes clay through a die and cuts it into bricks.
Step 5: Drying
Fresh bricks contain lots of water. They sit in drying chambers for 24-48 hours. This prevents cracking during firing.
Step 6: Firing
Dried bricks enter a kiln. The temperature reaches 900-1200 degrees Celsius. This takes several hours. The heat hardens the clay permanently.
Step 7: Cooling
Bricks cool down slowly inside the kiln. Rapid cooling would crack them. This takes another day or two.
Step 8: Sorting
Workers inspect finished bricks. They sort them by quality and color. Now the bricks are ready for construction.
That’s how clay becomes the bricks in our buildings.
Types of Bricks by Material and Use
Bricks come in different types. Each serves a specific purpose. Here’s a simple breakdown.
Types by Material:
| Brick Type | Main Materials | Key Features | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay Bricks | Natural clay | Strong and durable | Homes and buildings |
| Concrete Bricks | Cement, sand, aggregates | Cost-effective | Fences and garden walls |
| Sand Lime Bricks | Sand and lime | Light color, good sound insulation | Interior walls |
| Fire Bricks | Heat-resistant clay | Withstands high temperatures | Fireplaces and furnaces |
Types by Use:
| Brick Type | Purpose | Special Properties | Where You’ll See Them |
|---|---|---|---|
| Building Bricks | Standard construction | Good strength | Interior and exterior walls |
| Facing Bricks | Decorative finish | Smooth appearance, various colors | Outside of buildings |
| Engineering Bricks | Heavy-duty construction | Extra strong, water-resistant | Foundations and retaining walls |
| Paving Bricks | Ground surfaces | Wear-resistant | Driveways and pathways |
Each type fits a specific need. Choose based on what you’re building and where it goes.
How Long is a Brick? (Standard Brick Sizes)
Brick sizes vary by country and purpose. Let me show you the most common measurements.
| Brick Type | Length | Width | Height |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modular (US) | 7.625 inches | 3.625 inches | 2.25 inches |
| Queen | 9.625 inches | 3.125 inches | 2.75 inches |
| King | 9.625 inches | 2.75 inches | 2.625 inches |
| Standard (UK) | 215 mm | 102.5 mm | 65 mm |
| Jumbo | 12 inches | 4 inches | 3 inches |
Builders choose sizes based on the project. Larger bricks cover more area faster. Smaller bricks allow for detailed work.
The mortar joints between bricks also matter. Most calculations include a 0.375-inch mortar joint. This brings a standard brick to exactly 8 inches long when laid.
Most other countries use millimeters. Always check which system your supplier uses.
Now you know what to expect when buying bricks for your project.
Factors Affecting Brick Quality
Quality bricks depend on a few key factors. Here are the most important ones.
- Raw Material Quality: Pure clay makes strong bricks. Impurities create weak spots. The better the clay, the better the brick.
- Firing Temperature: This is critical. Bricks need 900-1200 degrees Celsius. Too low makes them weak. Too high causes warping.
- Molding Pressure: High pressure creates dense bricks. Dense bricks are stronger. Low pressure leaves air pockets that weaken them.
- Drying Process: Proper drying prevents cracks. Bricks need 24-48 hours to dry slowly. Rushing this step ruins quality.
- Cooling Rate: Slow cooling is essential. Fast cooling causes cracks. Bricks need one to two days to cool down properly.
- Water Content: The right amount of water matters. Too much causes cracking. Too little makes molding difficult.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Brickmaking affects the environment mainly through energy use, raw material extraction, and emissions, but modern methods are making it more sustainable.
Energy Use & Emissions
Traditional clay bricks are fired in kilns at 900–1,200°C, consuming large amounts of fuel and releasing CO₂ and other pollutants.
Newer technologies like tunnel kilns, biomass fuels, and waste-heat recovery systems reduce emissions and energy consumption.
Raw Materials
Extracting clay and shale can cause land degradation and soil loss. Many producers now use fly ash, recycled materials, and controlled mining to minimize damage.
Sustainable Alternatives
- Fly Ash Bricks: Made from industrial waste; no kiln firing.
- Compressed Earth Blocks (CSEB): Naturally cured, low energy.
- Calcium Silicate Bricks: Steam-cured, energy-efficient.
Longevity & Reuse
Bricks are durable, often lasting for decades. They can be reused or recycled, reducing construction waste.
The Bottom Line
Bricks are clay, water, sand, and heat combined into durable building blocks.
This blog covered their composition, manufacturing process, types, sizes, and quality factors.
Understanding these basics helps in making informed construction choices. Each brick type serves a specific purpose based on material and use.
The environmental impact is significant, but sustainable practices are improving the industry.