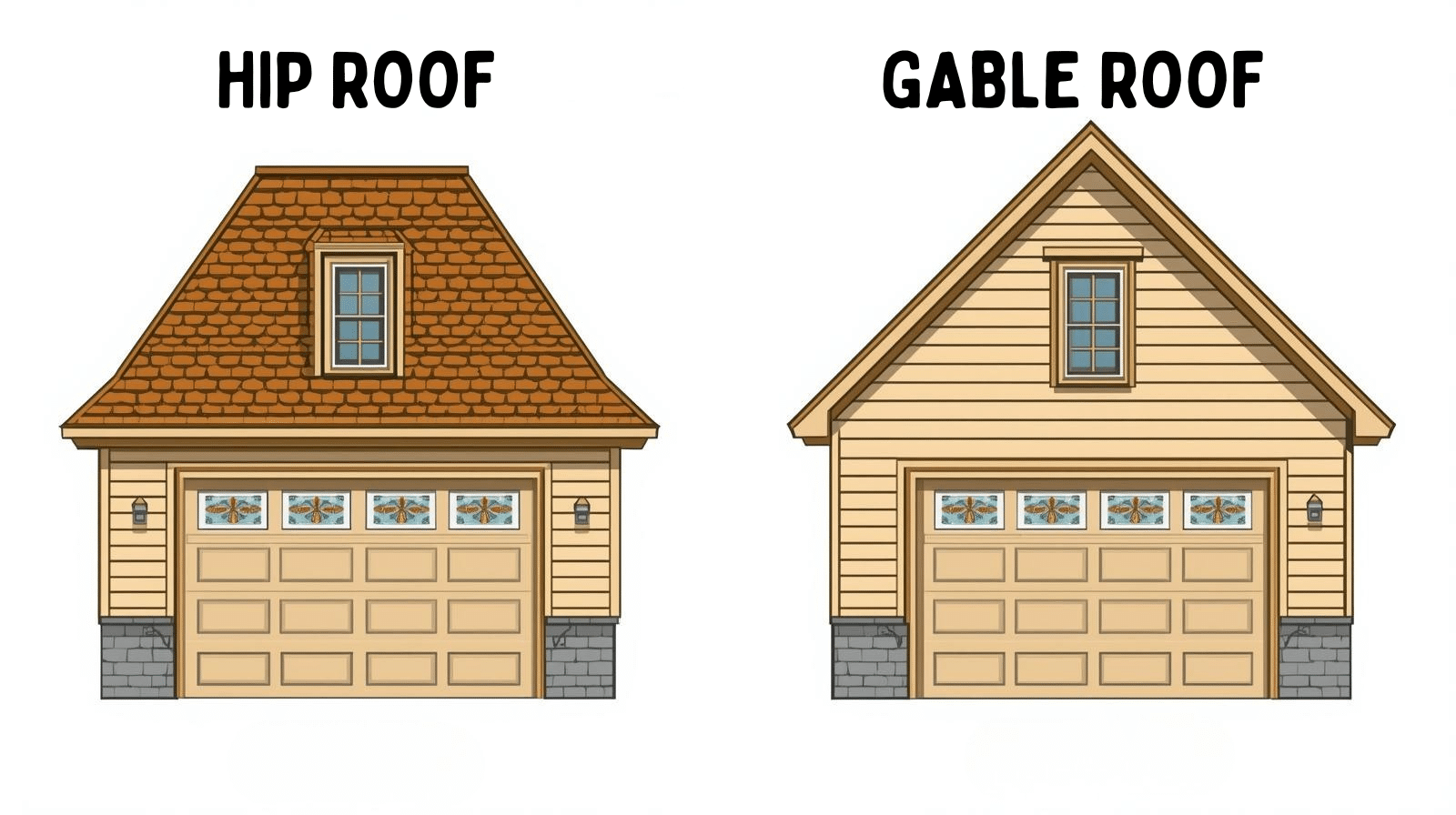
The gable roof vs hip roof debate is one of the oldest in construction, and both options have strong supporters.
This blog promises to break down the real differences between these two popular roof types. It shows which one works best for different climates, budgets, and building designs.
You will get practical comparisons on construction costs, weather resistance, and maintenance needs.
By the end, you’ll know exactly which roof style fits their next project and why it makes sense for their specific situation
Core Features and Design Basics
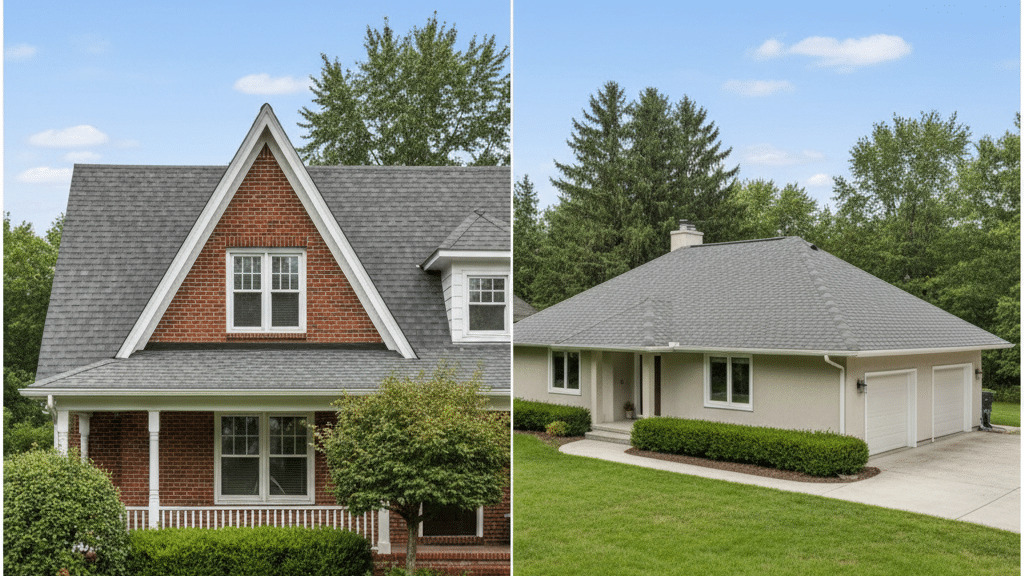
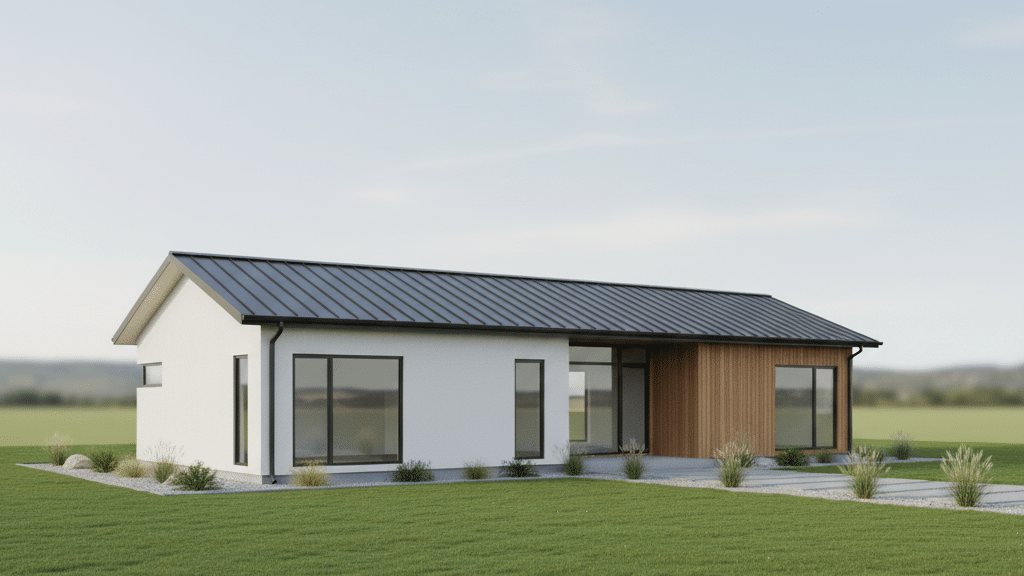
Gable roofs feature two sloping sides that meet at a ridge. They create a triangular shape that’s easy to spot.
The design is simple and builders can put it up quickly. This style offers great attic space and ventilation.
Hip roofs slope on all four sides. They meet at the top to form a ridge or point. All sides angle down toward the walls. This creates a more compact profile.
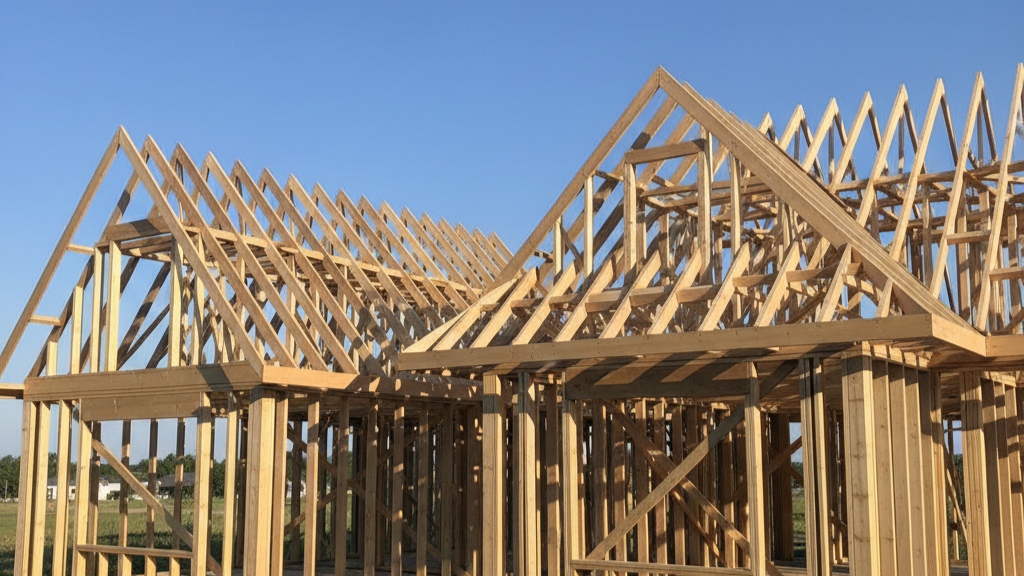
The main difference shows in the structure. Gable roofs need fewer materials and less labor. Hip roofs require more rafters and complex framing. They use extra lumber at every corner.
Both styles work with various materials. Shingles, tiles, and metal panels fit either design.
The choice depends on local weather and building codes. Each style has its place in modern construction.
Gable Roof vs Hip Roof – Head-to-Head Comparison
The right roof choice depends on several factors. Builders need to weigh design, cost, and performance before making a decision.
Here’s how these two styles stack up across key categories that matter most for construction projects.
1. Design Structure
Gable roofs use a straightforward two-sided design. Hip roofs need four sloping sides that connect at angles. The structural difference is clear from the ground up.
- Gable roofs have vertical end walls called gables
- Hip roofs slope inward from all sides
- Gable designs create open attic spaces
- Hip roofs form tighter, more compact profiles
- Both need proper ridge vents for airflow
2. Construction Complexity
Hip roofs demand more skill and time to build. Gable roofs go up faster with standard framing techniques. The labor costs reflect this difference.
- Gable roofs use simple rafter patterns
- Hip roofs require diagonal hip rafters
- Gable framing needs fewer cuts and measurements
- Hip roofs involve complex angle calculations
- Installation time differs by several days
3. Material Requirements
Hip roofs consume more materials than gable designs. The four-sided structure needs extra lumber and sheathing. This impacts the total project budget.
- Gable roofs use 15-20% less material
- Hip roofs need more ridge boards
- Gable designs require fewer corner pieces
- Hip roofs demand additional flashing
- Waste reduction favors gable construction
4. Ventilation Options
Gable roofs offer more ventilation choices. The end walls provide space for vents and windows. Hip roofs limit these options but still allow airflow.
- Gable ends accommodate louvered vents easily
- Hip roofs rely on ridge and soffit vents
- Gable designs allow larger attic windows
- Hip roofs need continuous ridge ventilation
- Both styles require balanced intake and exhaust
5. Cost Comparison
Hip roofs cost 15-25% more than gable roofs. The price difference comes from labor and materials. Budget constraints often determine the final choice.
- Gable roofs average $8-12 per square foot
- Hip roofs run $10-15 per square foot
- Labor accounts for the biggest cost gap
- Material waste adds to hip roof expenses
- Regional pricing varies based on local contractors
Advantages and Disadvantages
Every roof style comes with trade-offs. Builders need to understand both the benefits and drawbacks before committing to a design.
Gable Roof
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Lower construction costs save money on materials and labor | Wind can damage or lift gable ends during storms |
| Simple design makes building faster and easier | Less stable in hurricane-prone areas |
| More attic space for storage or living areas | Requires extra bracing in high-wind zones |
| Better natural ventilation through gable ends | Overhangs need proper support to prevent sagging |
| Easy to add dormers or windows later | Not ideal for areas with extreme weather |
| Water sheds quickly with fewer valleys | Insurance costs may be higher in coastal regions |
| Repairs and maintenance cost less over time | Limited design variety compared to hip roofs |
Hip Roof
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Superior wind resistance protects in storms | Higher construction costs increase project budget |
| More stable structure handles extreme weather | Complex design requires skilled contractors |
| Works well in hurricane and tornado zones | Less attic space due to sloping on all sides |
| Self-bracing design adds strength | More valleys mean more potential leak points |
| Better for areas with heavy snow loads | Ventilation options are more limited |
| Lower insurance premiums in some regions | Repairs take longer and cost more |
| Appealing look adds resale value | Harder to add dormers or modify later |
Factors to Consider Before Choosing the Type of Roof for Your Project
The roof decision affects more than just appearance.
Several practical factors should guide the choice between gable and hip roofs. Smart builders evaluate these elements before breaking ground.
- Local Climate Conditions – High-wind areas need hip roofs for stability while moderate climates handle gable roofs fine.
- Budget Constraints – Gable roofs cost less upfront and hip roofs require bigger initial investment with potential insurance savings.
- Building Codes – Some regions mandate specific roof types based on weather patterns and local regulations.
- Home Design Style – Traditional homes suit gable roofs while modern designs often feature hip roofs.
- Future Expansion Plans – Gable roofs allow easier additions and modifications compared to hip roof structures.
- Maintenance Preferences – Consider long-term upkeep costs and accessibility for repairs.
Variations and Hybrid Options for Modern Builds
Builders don’t have to choose just one style anymore.
Hybrid roof designs combine gable and hip elements for better performance. A hip roof with gabled ends offers wind resistance plus extra attic space. This combination works well in mixed climate zones.
Dutch gable roofs place a small gable on top of a hip roof section. They add charm while keeping structural benefits. Cross-gabled roofs use multiple gable sections at different angles.
These create visual interest in larger homes.
Some builders add a hip roof over the main structure and gable roofs over porches. This protects the house while saving money on covered areas.
Mansard and gambrel variations offer even more options. Each hybrid design serves specific needs.
The key is matching the roof to climate, budget, and style preferences.
Wrapping it Up
Both roof styles serve builders well in different situations. Hip roofs win in stormy climates with their superior wind resistance.
Gable roofs make sense when budgets are tight and attic space matters. The gable roof vs hip roof decision comes down to location, weather patterns, and project goals.
Don’t rush this choice. Talk to local contractors who know regional building codes. Check insurance requirements in your area. Consider how long you plan to keep the property.